Data driven stellar models
- Going beyond the synthetic stellar atmospheres combined with isochrones and extinction curves.
Goals of data driven models
We are now in an era where data are so precise that are physical models are systematically significantly wrong.
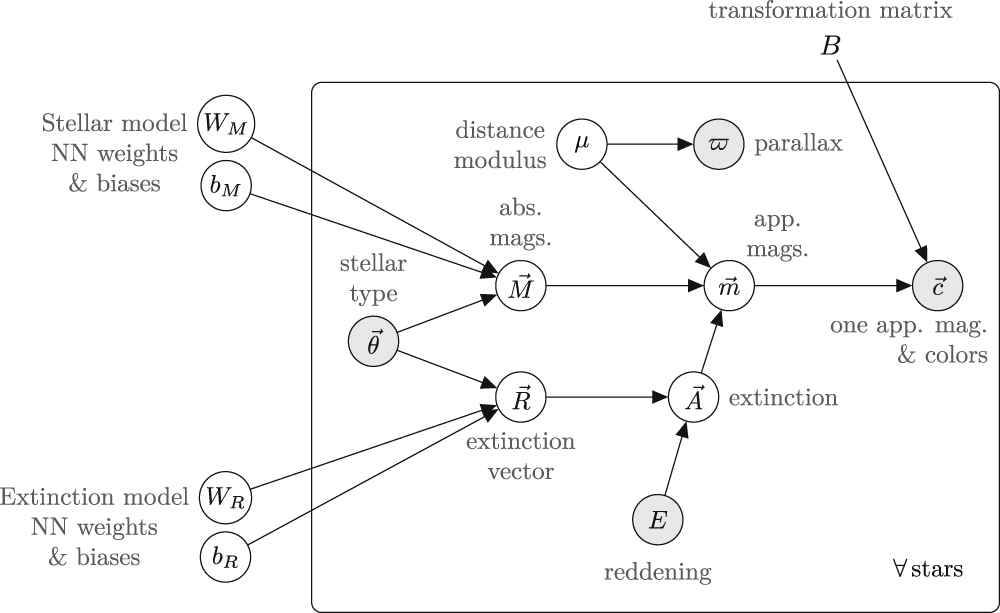
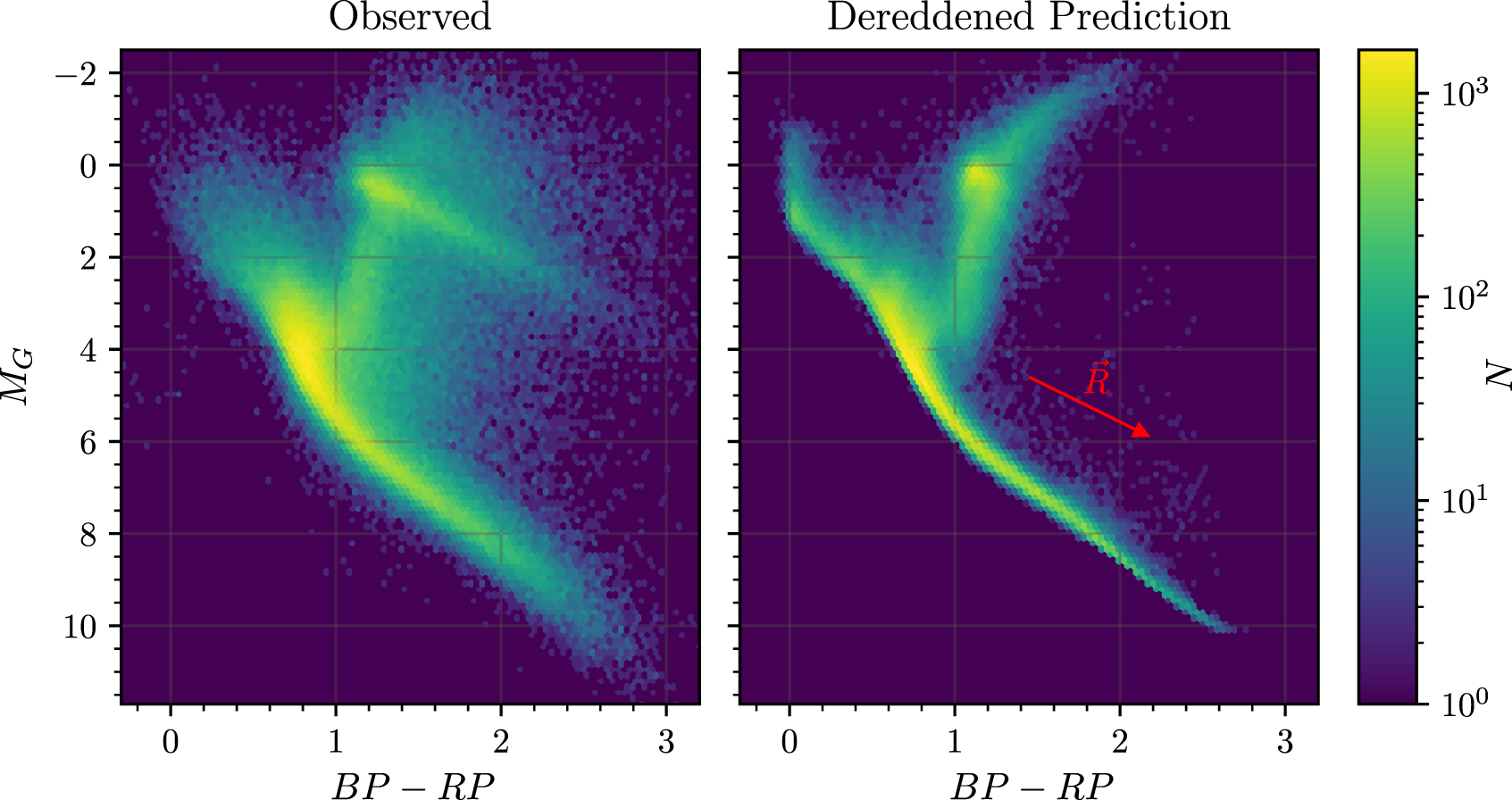
In Green et al. 2021, we developed a data-driven model to map stellar parameters ($T_{eff}$, $\log g$ , and [Fe/H]) accurately and precisely to broadband stellar photometry. This model must, and does, simultaneously constrain the passband-specific dust reddening vector in the Milky Way, $R$. The model uses a neural network to learn the (de-reddened) absolute magnitude in one band and colors across many bands, given stellar parameters from spectroscopic surveys and parallax constraints from Gaia. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach, we train our model on a data set with spectroscopic parameters from LAMOST, APOGEE, and GALAH, Gaia parallaxes, and optical and near-infrared photometry from Gaia, Pan-STARRS 1, Two Micron All Sky Survey and Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer. Testing the model on these data sets leads to an excellent fit and a precise—and by construction—accurate prediction of the color-magnitude diagrams in many bands. This flexible approach rigorously links spectroscopic and photometric surveys, and also results in an improved, Teff-dependent R. As such, it provides a simple and accurate method for predicting photometry in stellar evolutionary models. Our model will form a basis to infer stellar properties, distances, and dust extinction from photometric data, which should be of great use in 3D mapping of the Milky Way. Our trained model can be obtained at doi:10.5281/zenodo.3902382.